By
Dr. Yoga Nagender M
MBBS, MS – General Surgery, MCh – Pediatric Surgery, DNB – Pediatric Surgery
Consultant Pediatric Surgeon
Apollo Cradle, Kondapur
Posterior urethral valves (PUV) are thick prominent folds in urethra starting below veru montanum level which prevents a free flow of urine from the urinary bladder. As the PUV are blocking the urine passage back pressures are exerted on to the posterior urethra, urinary bladder, ureters and kidneys. Which starts obstructive damage to the child from prenatal period.
What decides the future of the child with PUV?
– Thick prominent valves
– Renal dysplasia
– Early Management
– Pop off mechanisms – Vesico ureteric reflux on one side, Urinoma, Bladder diverticulum
– Regular follow ups
What to expect after Prenatal detection of Posterior urethral valves?
If PUV are diagnosed during TIFFA scan and confirmed with oligohydramnios and lung hypoplasia, termination can be discussed during antenatal counseling with the pediatric surgeon. In addition to the Obstetrician, Pediatric surgeon will discuss the condition of the unborn child, planning of the perinatal management and the long term prognosis.
Evaluation after birth –
Palpable urinary bladder, high serum creatinine after 24 hours and poor stream of urine supports the clinical suspicion. Ultrasound KUB and Voiding cystourethrography ( VCU / MCUG) confirms the diagnosis of Posterior urethral valves.
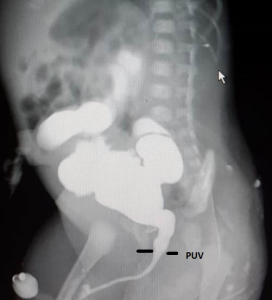
Management of PUV-
Fulguration of Valves- Cystoscopy and primary fulguration of valves is the gold standard treatment for PUV management. Fulguration of valves is the beginning of the treatment. Life long follow ups with the pediatric nephrologist and medical management is mandatory .
Vesicostomy- In few special situations vesiceostomy is done and a fulguration with vesicostomy closure are performed at a later date as decided by the treating pediatric surgeon.
End stage renal disease (ESRD) in PUV child possibility and management depends on the severity of the valve and pressure effects on the upper tracts as it is an irreversible change.